a.b.c.i = 99; // Throws a NullPointerExceptionJava 17
What’s new?
Better NullPointerExceptions
Garbage Collection Improvements
Text Blocks
Pattern matching for instanceof
Switch Expressions
Records
Sealed Classes
And more!
Better NullpointerExceptions
NullPointerException at Prog.main(Prog.java:5)NullPointerException: Cannot read field "c" because "a.b" is null ...Garbage Collection (GC)
GC Trade-offs
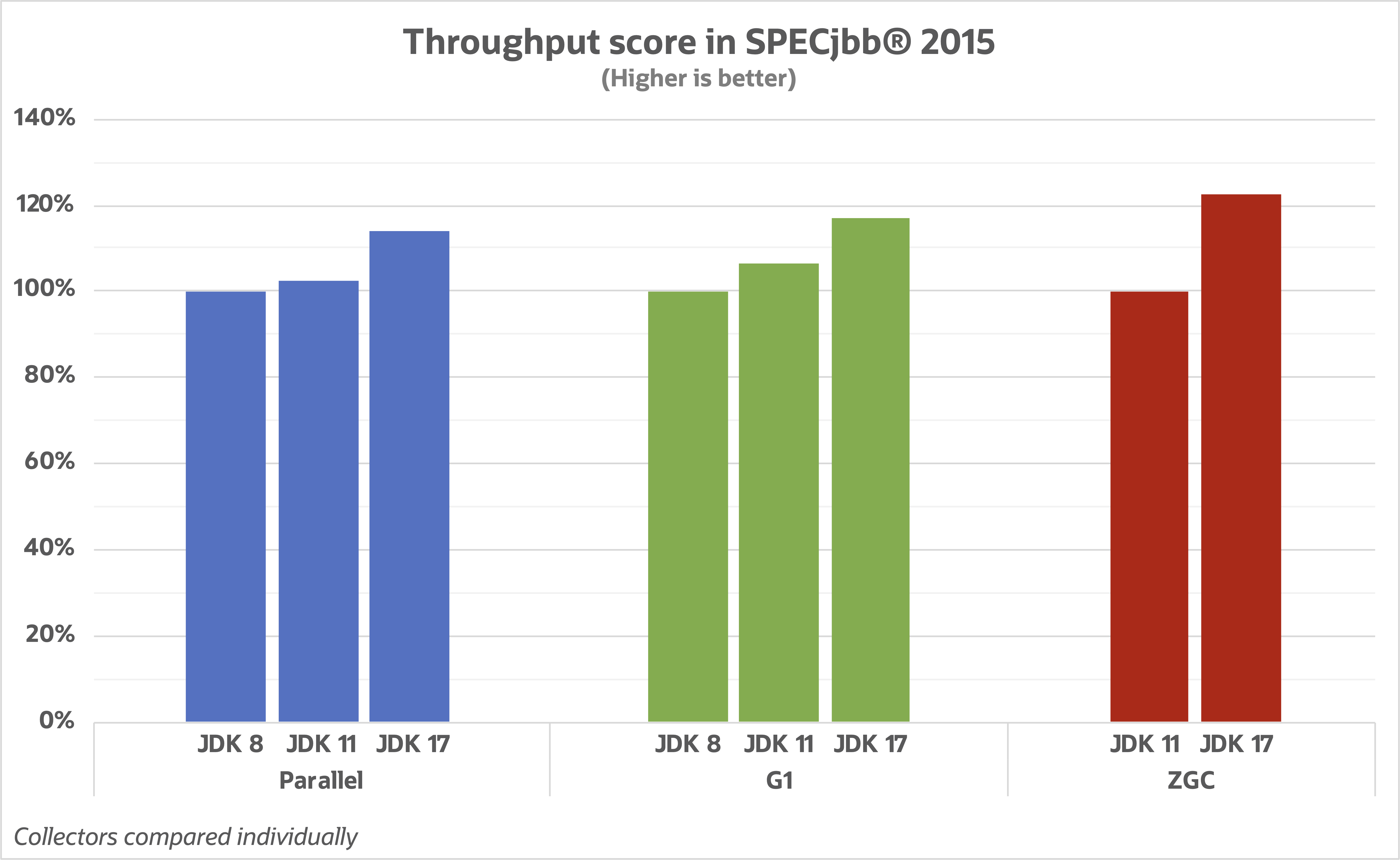
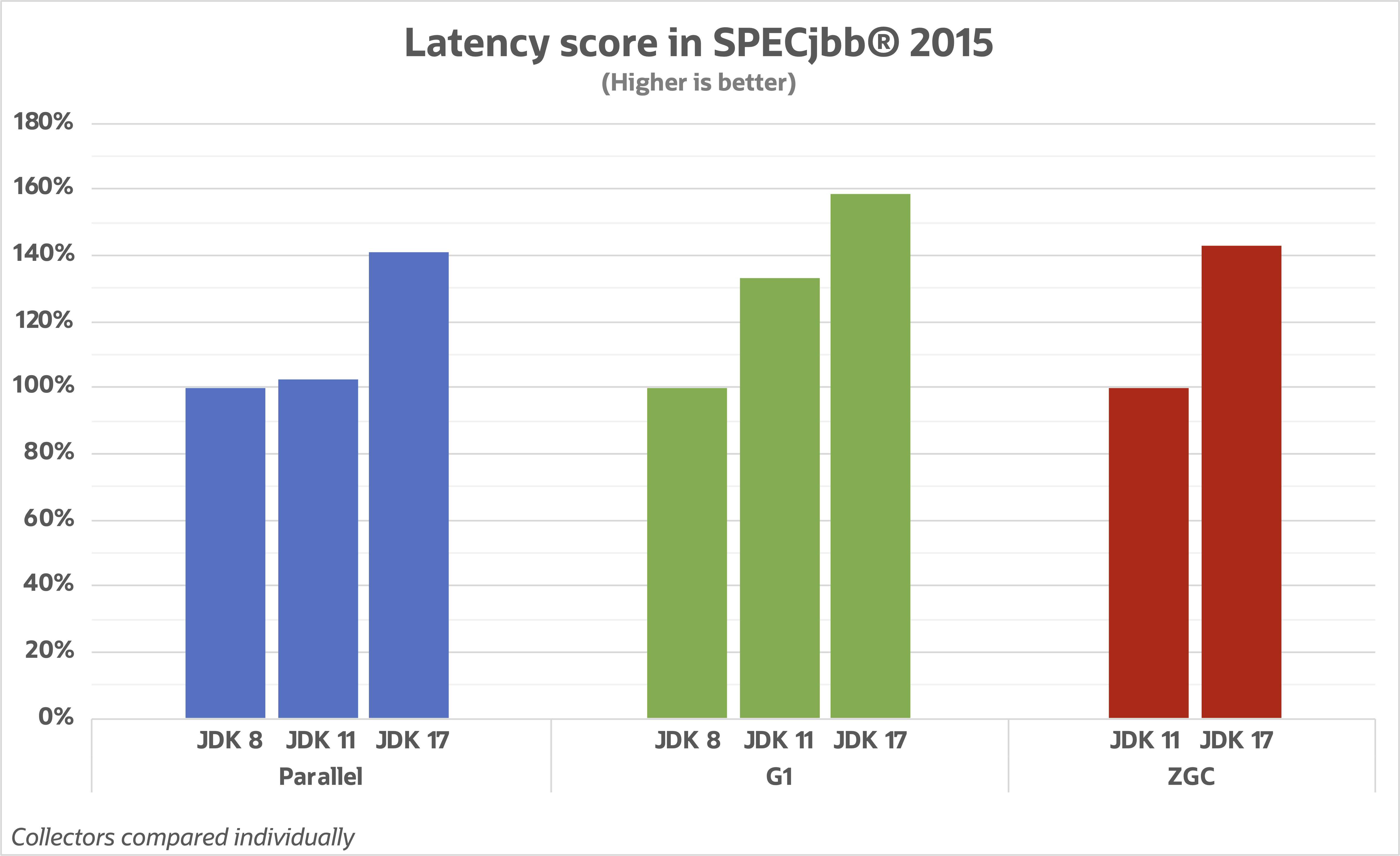
| Throughput | How much time is spent doing actual application work vs GC work? |
| Latency | How does GC affect individual app operations? |
| Footprint | How much extra memory is needed for the GC? |
Java GCs
| Serial | simple, single threaded |
| Parallel | throughput |
| G1 (default) | balance of throughput and latency |
| Shenandoah | latency |
| ZGC | latency |
| Epsilon | no-op collector |
Java 17 GC Benchmarks
Text Blocks
Indentation and Escaping
String grossJson = "{\n\"id\": 1,\n\"qty\": 5,\n\"price\": 1}";String prettyJson = """
{
"id": 1,
"qty": 5,
"price": 1
}
""";Long lines
String normalString = "This is a lot of text that "
+ "is meant to all be on the same line. "
+ "Which example looks better? "
+ "Which example looks more maintainable?";String textBlockString = """
This is a lot of text that \
is meant to all be on the same line. \
Which example looks better? \
Which example looks more maintainable?""";Pattern Matching for instanceof
Example 1
Object o = someRandomObject();
if (o instanceof String) {
String s = (String)o;
// do something with String s...
} else if (o instanceof Number) {
Number n = (Number)o;
// do something with Number n...
}Object o = someRandomObject();
if (o instanceof String s) {
// do something with String s...
} else if (o instanceof Number n) {
// do something with Number n...
}Example 2
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Point)) return false;
Point other = (Point) o;
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}public final boolean equals(Object o) {
return (o instanceof Point other)
&& x == other.x && y == other.y;
}Switch Expressions
int numLetters; // gross
switch (day) {
case MONDAY:
case FRIDAY:
case SUNDAY:
numLetters = 6;
break;
case TUESDAY:
numLetters = 7;
break;
// Thursday, Saturday, Wednesday...
}int numLetters = switch (day) {
// Arrows means no breaks needed, they don't "fall through"
case MONDAY, FRIDAY, SUNDAY -> 6;
case TUESDAY -> 7;
case THURSDAY, SATURDAY -> 8;
case WEDNESDAY -> 9;
}Expression returns a value
Must be exhaustive, but
defaultis not required
Switch statements
Switch statements do not have to be exhaustive (for backwards compatibility)
switch (day) {
case MONDAY -> System.out.println("Sounds like somebody's got a case of the Mondays!");
case FRIDAY -> System.out.println("Have a good weekend!");
}Records
final class Range {
private final int start;
private final int end;
Range(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
public int start() { return start; }
public int end() { return end; }
public boolean equals(Object o) { /*...*/ }
public int hashCode() { /*...*/ }
public String toString() { /*...*/ }
}record Range(int start, int end) { }Usage:
var range = new Range(2, 3);
System.out.println(range.start());
System.out.println(range.end);Record Properties
Immutable
Transparent
Can’t extend any class (implicitly extends record)
Can’t be extended
Can implement interfaces
Record Constructors
Automatically given
canonical constructorsAll constructors must ultimately call it
record Range(int start, int end) {
// Canonical constructor that uses the compact syntax
Range {
if (end < start) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("start must be less than end");
}
}
// Has to use the canonical constructor
Range(int end) { this(0, end); }
}Sealed Classes
class Shape { } // No limits to extensionfinal class Shape { } // Nothing can extendEnables more fine-grained inheritance control
sealed class Shape {
permits Circle, Rectangle, Triangle {
}
class Circle extends Shape { }
class Rectangle extends Shape { }
class Triangle extends Shape { }Data Oriented Programming
What happens when we combine these?
Pattern Matching
Switch Expressions
Records
Sealed Classes
AsyncResult Example
sealed interface AsyncResult<V> {
record Success<V>(V result) implements AsyncResult<V> { }
record Failure<V>(Throwable cause) implements AsyncResult<V> { }
record Timeout<V>() implements AsyncResult<V> { }
record Interrupted<V>() implements AsyncResult<V> { }
}AsyncResult<V> r = future.get();
switch (r) {
case Success<V>(var result): ...
case Failure<V>(Throwable cause): ...
case Timeout<V>(): ...
case Interrupted<V>(): ...
}Stream::toList
var nums = IntStream.range(0, 10)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.toList());var nums = IntStream.range(0, 10)
.boxed()
.toList();Conclusion
Java 17 improves…
System Performance
Enhanced garbage collectors
Developer Velocity
Better null pointer exceptions
Text blocks,
Stream::toListPattern matching, switch expressions, and records
Developer Flexibility
Sealed classes